Agriculture in SADC has opportunities for digital innovations that will lead to both benefits and risks, making the understanding of the ecosystem approach to digital transformation of key importance.
Credit: AgriTools Project 2015 – Elisabetta Demartis
Agriculture is of major social and economic importance in the SADC region, contributing between 2% and 27% of GDP and approximately 13% of overall export earnings (SADC, 2020, Selected Economic and Social Indicators 2019).
Approximately 70% of the region’s population, 363 million people in 2020 (UN, 2019, World Population Prospects) depend on agriculture for food, income, and employment.
It is more urgent than ever to ensure that agriculture feed the world’s growing population.
Conscious land use, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, judicious use of natural resources, improving climate resilience, and providing living wages to the millions of smallholder farmers who make a significant contribution to global food production must be prioritized.
All these factors have accelerated the aspiration by countries to kickstart a digital economy approach to increase efficiency in public sector operations but also to facilitate the introduction of digital solutions in the agricultural sector.
Opportunities for Digital Innovation in Agriculture
Credit: AgriTools Project 2015 – Elisabetta Demartis
The agriculture sector is ripe for innovative solutions to help tackle challenges of food security, hunger, inclusiveness, and sustainability at national, regional, and international levels.
Digitization is expected to play an increasingly significant role in achieving global food security, improving livelihoods in rural areas, and is undergoing expansion at an exponential rate.
Digital innovations and technologies have the potential to transform agri-food systems by accelerating and integrating stakeholders and their work across the value chain.
These solutions can:
- address low productivity,
- address supply chain inefficiencies by integrating traceability and logistics technologies,
- increase access to financial products and services through digital devices,
- and enhance resilience to climate change by using digital and precision data solutions to improve decision making on resource management allocations.
Digitalization is a gradual process that builds a functioning, dynamic and evolving digital ecosystem

Credit: AgriTools Project 2015 – Elisabetta Demartis
Digitalization implies the use of digital technologies, innovations, and data to transform business models and practices across the value chain and address bottlenecks to achieve greater incomes for smallholder farmers, improve food and nutrition security, build climate resilience, and expand the inclusion of youth and women.
Digital transformation promises positive outcomes, such as efficiency, cost savings, and convenience, and increased trust in remote transactions.
It also brings barriers and risks that could negatively affect the adoption of digital solutions, such as cyber threats, fraud, exclusion of marginalized populations, and lack of emphasis on sustainability.
The process requires a broadly established and well-understood internal rationale, changes to organizational mindsets, ways of working and behaviors, and staff with the appropriate investment of time and resources.
An Ecosystem Approach
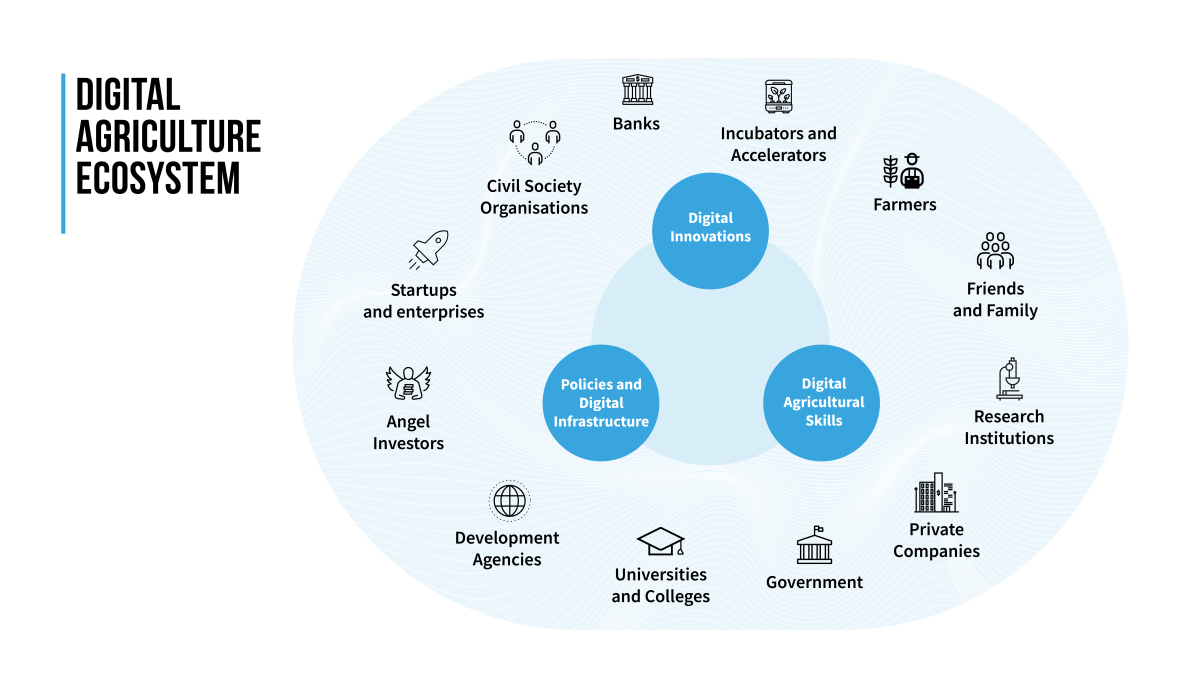
Credit: Diagram - IMC Worldwide, Icons - the NounProject 2022
The digital agriculture ecosystem made up of policies and infrastructure, digital innovations and digital agriculture skills surrounded by the relevant ecosystem stakeholders.
Achieving and sustaining any agricultural outcome often depends on the ability of multiple interconnected actors to work together.
Adopting an ecosystem approach recognizes the different actors, relationships and resources that have important roles in scaling innovations.
A digital ecosystem comprises stakeholders, systems, and an enabling environment that empowers communities to use digital technology to access services, engage with one another and drive economic advancement.
Key actors within an ecosystem include governments, civil society, private sector, universities, and innovators to work effectively together.
For innovations to be successful, they must be efficiently generated, developed, tested, reiterated, refined, and ultimately scaled for development impact within an enabling environment.
The ecosystem in which innovation exists requires coordination, collaborative action, and resources to ensure that it can operate at multiple levels - local, national, and regional - and inclusive of relevant sectors.
A global digital revolution is underway where the opportunities of Agriculture, the need for employees with digital skills and greater infrastructure and policies will need to be prioritized. This is epitomized by farmers in need of dynamic digital information on the prices of different commodities, the acceleration of online e-commerce and increasing use of Internet of Things (IoT) and robotics in all sectors including Agriculture.
For more information on these themes and what implications digital transformation may have in agriculture in the SADC region, download full report, country profiles or associated data.
Icons - credit to NounProject https://thenounproject.com/







